Optical Filters
Definition: devices with a wavelength-dependent transmission or reflectance
More specific terms: interference filters, dichroic mirrors, rugate filters, etalons, Fabry–Pérot interferometers, diffraction gratings, birefringent tuners, acousto-optic tunable filters, cold mirrors, hot mirrors
German: optische Filter
How to cite the article; suggest additional literature
Author: Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta
An optical filter is usually meant to be a component with a wavelength-dependent (actually frequency-dependent) transmittance or reflectance, although there are also filters where the dependence is on polarization or spatial distribution, or some uniform level of attenuation is provided. Filters with particularly weak wavelength dependence of the transmittance are called neutral density filters.
Types of Optical Filters
There are many different types of optical filters, based on different physical principles:
Absorption Filters
Absorbing glass filters, dye filters, and color filters are based on wavelength-dependent absorption in some material such as a glass dopant, dye, pigment or semiconductor. As the absorbed light is converted into heat, such filters are usually not suitable for high-power optical radiation.
Interference Filters
Various kinds of optical filters are based on interference effects, combined with wavelength-dependent phase shifts during propagation. Such filters – called interference filters – exhibit wavelength-dependent reflection and transmission, and the light which is filtered out can be sent to some beam dump, which can tolerate high optical powers. An important class of interference-based filters contains dielectric coatings. Such coatings are used in dielectric mirrors (including dichroic mirrors), but also in thin-film polarizers, and in polarizing and non-polarizing beam splitters. Via thin-film design it is possible to realize edge filters, low-pass, high-pass and band-pass filters, notch filters, etc. The same physical principle is used in fiber Bragg gratings and other optical Bragg gratings such as volume Bragg gratings. Apart from step-index structures, there are also gradient-index filters, called rugate filters. That approach allows one to make high-quality notch filters, for example.
Fabry–Pérot interferometers, etalons and arrayed waveguide gratings are also based on interference effects, but sometimes exploiting substantially larger path length differences than monolithic devices. Therefore, they can have sharper spectral features.
Lyot Filters
Lyot filters involve wavelength-dependent polarization changes. Similar devices are used as birefringent tuners in tunable lasers.
Refractive and Diffractive Filters
Other filters are based on wavelength-dependent refraction in prisms (or prism pairs) or on wavelength-dependent diffraction at gratings, combined with an aperture.
Acousto-optic Filters
There are acousto-optic tunable filters, where it is exploited that Bragg reflection at an acoustic wave works only within a narrow frequency range.
Different Filter Shapes
Concerning the shape of the transmission curve, there are
- bandpass filters, transmitting only a certain wavelength range
- notch filters, eliminating light of a certain wavelength range, e.g. by reflecting it
- edge filters, transmitting only wavelengths above or below a certain value (high-pass and low-pass filters)
Of course, a wide range of filter shapes can also be realized, particularly with interference filters.
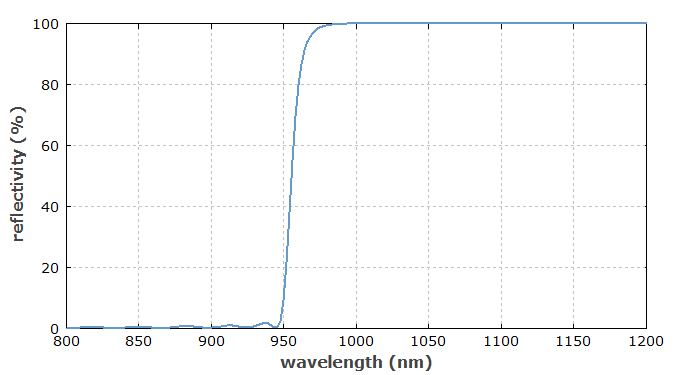
Applications
Some examples for the many applications of optical filters are:
- Filters can eliminate some unwanted light. For example, eye protection against laser radiation is often done with filters which can eliminate e.g. infrared laser light while transmitting visible light (→ laser safety). Similarly, sun glasses attenuate visible light and filter out ultraviolet light. Green laser pointers are often equipped with filters for removing residual infrared light. Heat control filters in the form of cold mirrors are used to transmit visible light while removing intense infrared radiation, as it is emitted e.g. by hot surfaces. Similarly, hot mirrors can remove infrared light from a beam path by reflecting it. Sharp edge filters or bandpass filters can be used in fluorescence microscopes for removing pump light from the fluorescence signal light.
- Wavelength-dependent losses are useful for gain equalization of fiber amplifiers, as used in optical fiber communications. Similarly, filters can be used for balancing a photodetector response or the non-uniform optical spectrum of a light source.
- In the image sensors of photo cameras, for example, RGB filters allow for separate detection of the intensity in different colors, so that color images are obtained.
- Filters in the form of fiber-optic add–drop multiplexers can extract or inject single channels in wavelength division multiplexing optical data transmission systems.
- Intracavity filters in lasers can be used for wavelength tuning and for single-frequency operation of lasers, or for suppressing lasing at unwanted wavelengths.
- Filters can suppress effects of amplified spontaneous emission in amplifier chains.
- The combination of a tunable filter and a broadband photodetector can be used for the spectral analysis of optical signals.
- Neutral density filters are used for attenuating optical signals without modifying their spectral shape.
Suppliers
The RP Photonics Buyer's Guide contains 229 suppliers for optical filters. Among them:

Technica Optical Components
World leader in Fiber Bragg grating and Fabry Perot filters. Product portfolio includes athermal Fabry–Perot etalons (TWR30) and athermal FBGs (TWR50), as well as tunable FBGs (T10-T980) and tunable Fabry–Perot filters (TFP10-TFP50).

TeraXion
Ultra narrow tunable optical filters for Brillouin filtering in remote sensing applications or for the isolation of a modulated RF signal in RF communications.


VisiMax Technologies
VisiMax process color filters selectively and accurately pass light of a small range of colors while reflecting other colors. Our heat-resistant dichroic filter coating technology produces durable interference filters that render light with precise spectral control.
Accelerate your project by choosing a standard VisiMax color filter, or utilize the expertise of our skilled design team to create a custom filter to meet your specific spectral requirements.


Edmund Optics
Edmund Optics offers a variety of optical filters for many applications, including bandpass interference, notch, edge, dichroic, color substrate, or ND. Edmund Optics also offers highly durable hard coatings for applications that require high optical densities with maximum performance.

Shanghai Optics
Shanghai Optics manufactures a wide range of custom optical filters for engineering, scientific, and photographic applications.


Artifex Engineering
Artifex Engineering offers custom absorption filters and dieletric filters in almost any design. Bandpass, long pass, short pass or ND filters can be tailored to your wavelength range. The filters can be cut to any shape. Black anodized aluminium rings may be provided for ease of mounting. Visit our product page for more information. We look forward to your inquiry.


Iridian Spectral Technologies
Iridian Spectral Technologies is a leading global supplier for applications in telecommunications, spectroscopy (Raman, fluorescence, and flow cytometry), biomedical imaging, endoscopy imaging, sensing, display and entertainment (glasses for 3D cinema, display coatings). Our optical filters and coatings cover the spectral range from UV 300 nm to LWIR 10 μm. Our products include narrow bandpass filters, steep edge long- or shortpass filters, dichroic edge filter, notch filter, multi-zone filter and other special coating filters.

EKSMA OPTICS
Crystalline material UV band pass filters, neutral density reflective type filters designed to operate at 400–2000 nm range, neutral density absorption type filters designed to operate at VIS (450–650 nm) and Schott color glass filters.


Dynasil
Optometrics, a Dynasil company, designs and manufactures long wavepass filters from 500 nm to 1500 nm in increments of 50 nm. These long wavepass filters are mounted in a black anodized aluminium ring. The cut-on wavelengths can be fine tuned by changing the angle of incidence. Optometrics also has short wavepass filters from 450 nm to 1000 nm in increments of 50 nm and otherwise similar characteristics. These filter types can also be used in combination for custom bandpass filtering.
EMF, also a Dynasil company, manufactures a custom line of Optivex™ dichroic filters that block 99% of harmful UV radiation while transmitting high-quality visible light with virtually no distortion. Optivex™ has been the product of choice for over 25 years, and its name is synonymous with absolute protection.

Knight Optical
Our stock and custom-made optical filters are employed for a wide range of high-tech applications by discerning engineers and R&D professionals within sectors such as military & defence, electronics and research markets. With both stock and custom-made filters available, our collection includes bandpass, longpass, shortpass, neutral-density (ND), dichroic, IR-cut, colour glass, heat glass and ANPR/ALPR filters.
Questions and Comments from Users
Here you can submit questions and comments. As far as they get accepted by the author, they will appear above this paragraph together with the author’s answer. The author will decide on acceptance based on certain criteria. Essentially, the issue must be of sufficiently broad interest.
Please do not enter personal data here; we would otherwise delete it soon. (See also our privacy declaration.) If you wish to receive personal feedback or consultancy from the author, please contact him e.g. via e-mail.
By submitting the information, you give your consent to the potential publication of your inputs on our website according to our rules. (If you later retract your consent, we will delete those inputs.) As your inputs are first reviewed by the author, they may be published with some delay.
See also: interference filters, neutral density filters, rugate filters, tunable optical filters, volume Bragg gratings, acousto-optic tunable filters, hot mirrors, cold mirrors, wavelength tuning, gain equalization, optical fiber communications
and other articles in the category photonic devices
 |



If you like this page, please share the link with your friends and colleagues, e.g. via social media:
These sharing buttons are implemented in a privacy-friendly way!