Giles Parameters
Definition: spectroscopic data concerning absorption and amplification in an active fiber
German: Giles-Parameter
Categories: fiber optics and waveguides, optical amplifiers, methods
How to cite the article; suggest additional literature
Author: Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta
For modeling the performance of fiber amplifiers made from rare-earth-doped fibers, so-called Giles parameters are often used. These comprise two wavelength-dependent quantities: the absorption coefficient α(λ) of the fiber with all laser-active ions in the ground state, and the gain coefficient g*(λ) for the fiber with all laser-active ions in the upper laser level. (The star may be interpreted as indicating the fully excited fiber.)
The Giles parameters are directly related to the transition cross sections of the laser transition and the overlap coefficients Γ(λ) of the fiber modes:
These equations are based on the assumption that the doping concentration is constant within some volume and zero outside it. However, they can be easily generalized for smooth doping profiles.
Of course, the equations are based on the assumption that only the laser transition contributes to gain or loss in the considered wavelength range. Parasitic background losses due to absorption and scattering in the fiber can be treated separately. Possible additional effects from excited-state absorption should be kept in mind.
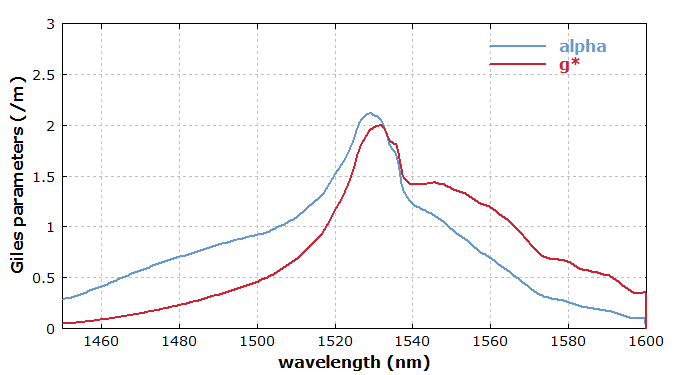
In practice, it is often difficult to precisely determine the dopant concentration ndop, the overlap coefficients Γ(λ) and the transition cross sections of a fiber. However, the Giles parameters can be obtained directly from measurements of absorption and gain. (A difficulty for the gain, however, is that one may not achieve full excitation of the laser-active ions.) Amplifier models may then directly be based on the Giles parameters rather than on the not precisely known values of ndop, Γ(λ), σabs(λ) and σem(λ).
Questions and Comments from Users
Here you can submit questions and comments. As far as they get accepted by the author, they will appear above this paragraph together with the author’s answer. The author will decide on acceptance based on certain criteria. Essentially, the issue must be of sufficiently broad interest.
Please do not enter personal data here; we would otherwise delete it soon. (See also our privacy declaration.) If you wish to receive personal feedback or consultancy from the author, please contact him e.g. via e-mail.
By submitting the information, you give your consent to the potential publication of your inputs on our website according to our rules. (If you later retract your consent, we will delete those inputs.) As your inputs are first reviewed by the author, they may be published with some delay.
Bibliography
| [1] | C. R. Giles and E. Desurvire, “Modeling erbium-doped fiber amplifiers”, IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 9 (2), 271 (1991), doi:10.1109/50.65886 |
See also: rare-earth-doped fibers, fiber amplifiers
and other articles in the categories fiber optics and waveguides, optical amplifiers, methods
 |



If you like this page, please share the link with your friends and colleagues, e.g. via social media:
These sharing buttons are implemented in a privacy-friendly way!